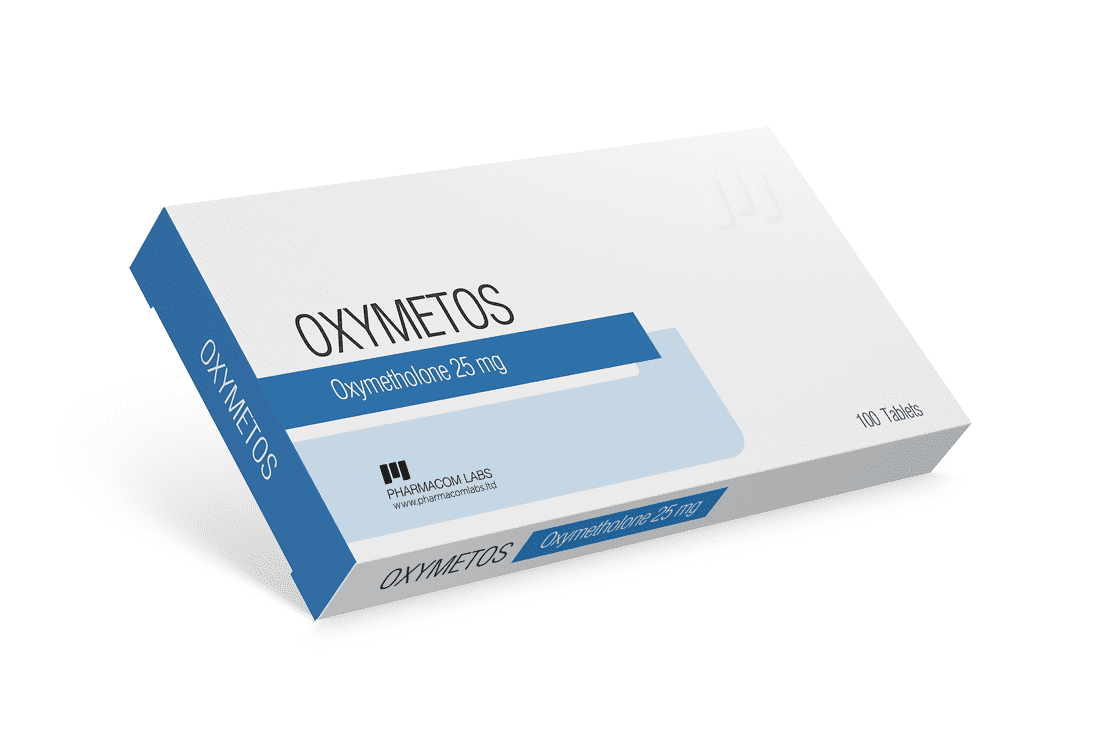
Oxymetholone (Anadrol / Anapolon)
Oxymetholone is a potent synthetic oral anabolic steroid, classified as a 17-alpha-alkylated derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Originally developed for the treatment of anemia, osteoporosis, and to support muscle growth in undernourished or debilitated patients, it was approved for human use by the U.S. FDA. However, with the emergence of more effective non-steroidal treatments for anemia and osteoporosis, oxymetholone’s medical application declined, leading manufacturers—most notably Syntex in 1993—to discontinue its production.
Performance and Effects
Oxymetholone is known for delivering extremely rapid and dramatic gains in muscle mass and strength, often comparable to methandienone (Dianabol). Like Dianabol, a significant portion of the weight gained is due to intracellular water retention, which can lead to side effects such as elevated blood pressure during a cycle.
Athletes frequently report a pronounced “pumping” effect due to oxymetholone’s ability to increase red blood cell count and overall blood volume. This intense muscular engorgement can be so powerful that it may hinder training by causing premature muscle fatigue or discomfort early in the workout.
Estrogenic Activity
Despite being a DHT derivative—which typically resists conversion to estrogen—oxymetholone exhibits notable estrogenic effects. This is not due to aromatization (as it cannot be converted to estradiol via the aromatase enzyme), but likely due to direct interaction with estrogen receptors. Because of this, aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are ineffective in controlling related side effects. Instead, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), such as Tamoxifen, are required to combat symptoms like gynecomastia or water retention.
There has been speculation that oxymetholone may possess progestogenic properties, similar to nandrolones, which could explain some of its estrogen-like side effects. However, clinical data do not support any significant progestogenic activity.
Key Characteristics
Chemical class: 17α-alkylated DHT derivative
Primary effects: Rapid muscle gain, strength increase, enhanced red blood cell production
Water retention: High
Estrogenic activity: Present, but non-aromatizing
Aromatase inhibitors: Ineffective
Antiestrogens (SERMs): Effective for side effect management
Progestogenic activity: None observed in medical studies
Medical use: Previously for anemia, osteoporosis, and wasting conditions (largely replaced)




There are no reviews yet.